While Gasification and incineration are both thermal processes, it is important to point out the advantages of Gasification over incineration. Incineration is simply a mass burn technology with heat recovery to produce steam and/or electricity. It has negative connotations because during the direct combustion of the waste, dangerous carcinogenic compounds such as dioxins and furans are formed, which might be discharged into the atmosphere unless very expensive scrubbing equipment is installed. This makes incineration technologies expensive to construct.
In contrast, Gasification employs the conversion of waste into a syngas, which can then be used for generating electricity. The syngas is produced under controlled conditions and is generated without the formation of impurities associated with incinerator flue gas.
Gasification emissions are generally an order of magnitude lower than the emissions from an incinerator.
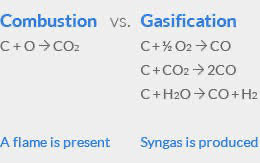
In order to understand the advantages of Gasification when compared to incineration, it’s important to understand the differences between the two processes:
Incineration literally means to render to ash. Incineration uses MSW as a fuel, burning it with high volumes of air to form carbon dioxide and heat. In a waste-to-energy plant that uses incineration, these hot gases are used to make steam, which is then used to generate electricity.
Gasification converts MSW to a usable synthesis gas, or syngas. In the Gasification process, the MSW is not a fuel, but a feedstock for a high temperature chemical conversion process. Instead of producing just heat and electricity, the syngas produced by Gasification can be turned into higher value products such as a substitute natural gas.